Hola amigo! 😊 Cómo estás hoy,
I would like to share a small part of my learnings from my first ever official project: POS/EDC machine integration with our billing system. This was an exciting challenge where I got hands-on experience working with APIs and vendors.
How does a Payment Machine actually work?
It's simple, start by initiating/creating a transaction, then retrieve its payment status.
Here, initiate/create refers to POST method and Retrieve refers to GET.
Workflow...
Let us assume that the vendor has given us a document with both these APIs (Create and Fetch Payment Status). Samples listed below -
CREATE TRANSACTION:
url/endpoint: https://payvendor.com/create-transaction
method: POST
payload:
{
"reference_id": "2345678",
"pos_id": "PISC98765",
"date_time": "MMDDYYYYHHMMSS"
"amount": 100
}
response: [200]
{
"reference_id": "2345678",
"pos_id": "PISC98765",
"date_time": "MMDDYYYYHHMMSS"
"unn": "456789876546787656"
}
FETCH PAYMENT STATUS:
url/endpoint: https://payvendor.com/get-status
method: GET
payload: ?reference_id="2345678"
response: [200]
{
"reference_id": "2345678",
"pos_id": "PISC98765",
"date_time": "MMDDYYYYHHMMSS"
"unn": "456789876546787656"
"status": "paid"
"amount": 100
}
How do we use these APIs? Let's find out... 🫡
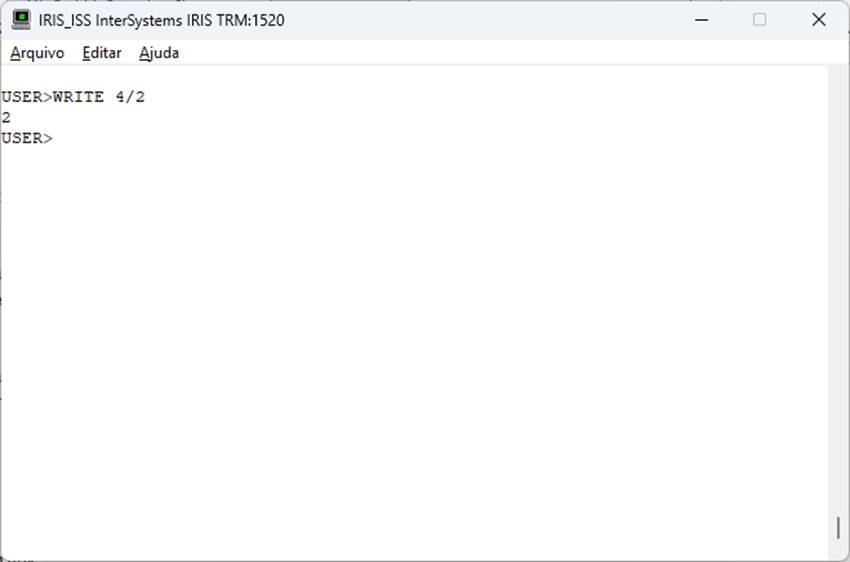
To consume these APIs in cache objectscript, we have a module or a class to make HTTP requests from within. %Net.HttpRequest.
Basic:
- Create an instance of %Net.HttpRequest.
- Set the url and the HTTP method.
- Add the header and the body. [if needed]
- Send the request to the server.
- Handle the response.
Set req = ##class(%Net.HttpRequest).%New()
Set req.Server = "https://payvendor.com"
Set req.Location = "/create-transaction"
Set req.Https = 1
Set req.ContentType = "application/json"
Set obj = ##class(%DynamicObject).%New()
Set obj."reference_id" = "2345678"
Set obj."pos_id" = "PISC98765"
Set obj."date_time" = $ZSTRIP($ZDATETIME($HOROLOG,8), "*P")
Set obj."amount" = 100
Do req.EntityBody.Write(obj.%ToJSON())
Do req.Post()
Write req.HttpResponse.StatusCode,!
Write req.HttpResponse.Data.Read(),!
After creating the transaction, we can maintain a table (preferred) or a global to maintain logs against each transaction.
Set req = ##class(%Net.HttpRequest).%New()
Set req.Server = "https://payvendor.com"
Set req.Location = "/get-status"
Set req.Https = 1
Do req.SetParam("reference_id", "2345678")
Do req.Get()
Set stsCode = req.HttpResponse.StatusCode,!
If stsCode=200 {
Set objResponse = req.HttpResponse.Data.Read()
Set objData = ##class(%DynamicObject).%FromJSON(objResponse)
Set payStatus = objData.status
}
This is how we fetch the payment status. After we fetch the status, we can update the same in the billing system and our logs too.
This workflow is simple, but as we code more, we can evolve better frameworks and approaches. Over my experience, I’ve successfully integrated 5 POS vendors and 3 payment gateways with our billing system. If you have any questions or need guidance, feel free to reach out!
Also open for feedback. :)
Thanks...